Disruption Potential of Injectable Anti-Obesity Therapies and Beyond
In 2024, the conversation around injectable anti-obesity therapies shifted from niche pharmaceutical innovation to a catalyst for sweeping industry change.
The PDA Universe of Pre-Filled Syringes and Injection Devices Conference outlined how these breakthrough treatments are disrupting drug delivery systems, reshaping market dynamics and influencing sectors far beyond healthcare. This article distills key insights and weaves in the latest updates on device technologies—both those already in patients’ hands and those still in development.
Disruption in Drug Delivery
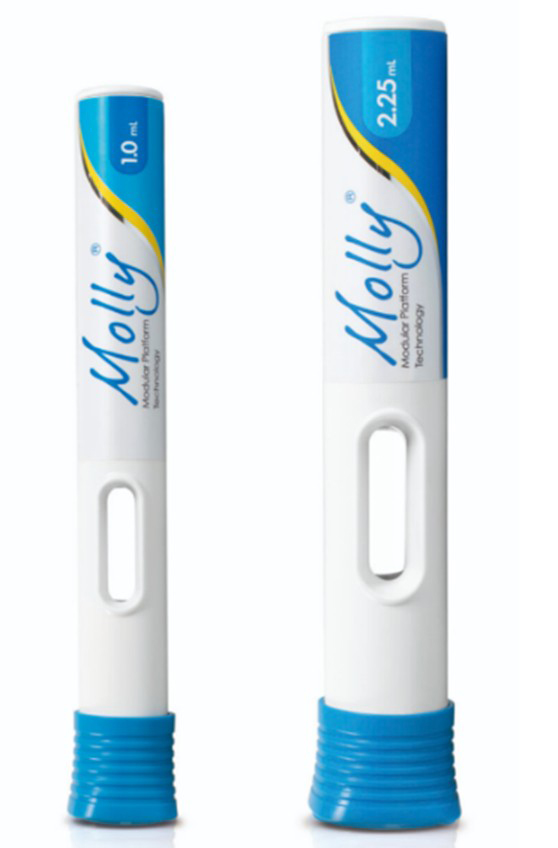
Images used with permission from SHL Medical.
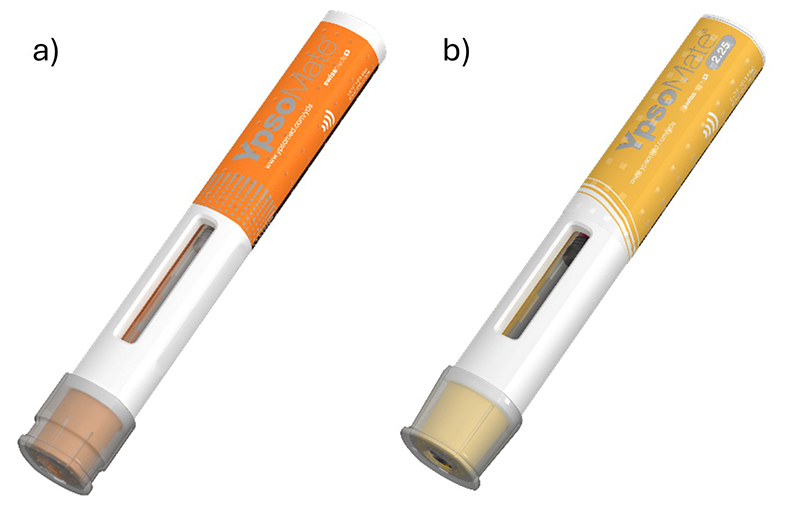
Ypsomed, the Ypsomed logo, and YpsoMate® are trademarks of Ypsomed AG. © 2025 Ypsomed AG. All rights reserved. Product images shown are the property of Ypsomed AG and used with permission.
Disruption in drug delivery refers to radical shifts in established industries or markets driven by technological innovation. The rise of new injectable anti-obesity drugs—most notably glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists—exemplifies this change. Products such as Zepbound (tirzepatide) and Wegovy (semaglutide), administered via weekly subcutaneous injections, have demonstrated significant weight-loss efficacy, with studies reporting reductions of 15–25%. In the United States (US), these treatments are typically delivered using disposable, prefilled-syringe (PFS)-based, single-use auto-injectors. Notable examples with potential applications in GLP-1 administration, both currently on the market and in development, include Molly® by SHL Medical (1) and Ypsomate by Ypsomed (2)—disposable auto-injectors depicted in Figure 1 and Figure 2 (3).
Market Impact and Growth
The market for GLP-1 agonist drugs is projected to grow exponentially, with sales expected to reach $100-150 billion by 2030, split equally between obesity and diabetes patients. In the US alone, 30 million patients are anticipated to be on GLP-1s by 2030, representing 9% of the population. This growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of obesity, which is projected to affect over 1 billion people worldwide by 2030.
Strategic Evolution of Drug Delivery Systems for GLP-1 Therapies
While disposable PFS-based auto-injectors have become the standard for GLP-1 delivery in the US, the projected scale of demand—1.5 billion devices annually for 30 million patients—necessitates a broader exploration of delivery modalities. Each alternative offers unique advantages and challenges in terms of usability, cost, sustainability and clinical effectiveness, as illustrated in the table below.
| PRODUCT | PROS | CONS |
|---|---|---|
| Reusable Auto-Injectors (example: Elexy™, a reusable auto-injector by SHL Medical shown in Figure 3 and YpsoPen®, a reusable pen injector by Ypsomed shown in Figure 4a) |
|
|
| Cartridge-Based Pens (example: YpsoFlowTM by Ypsomed shown in Figure 4b) |
|
|
| Oral Delivery |
|
|
| Nasal Delivery |
| |
| Implants |
|
|
| Depot Injections (Long-Acting Injectables) Description: Intramuscular or subcutaneous injections that release the drug over weeks or months. |
|
|
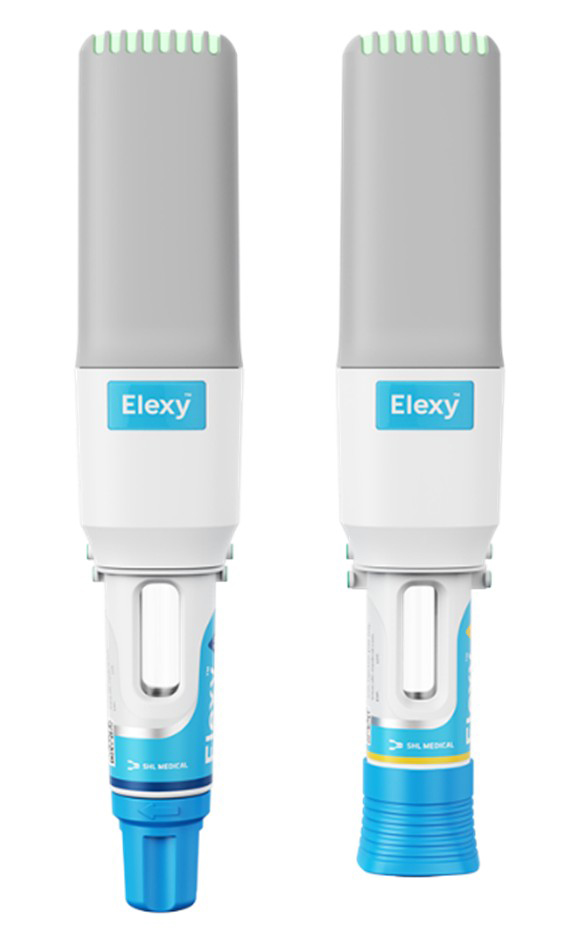

Images used with permission from SHL Medical.
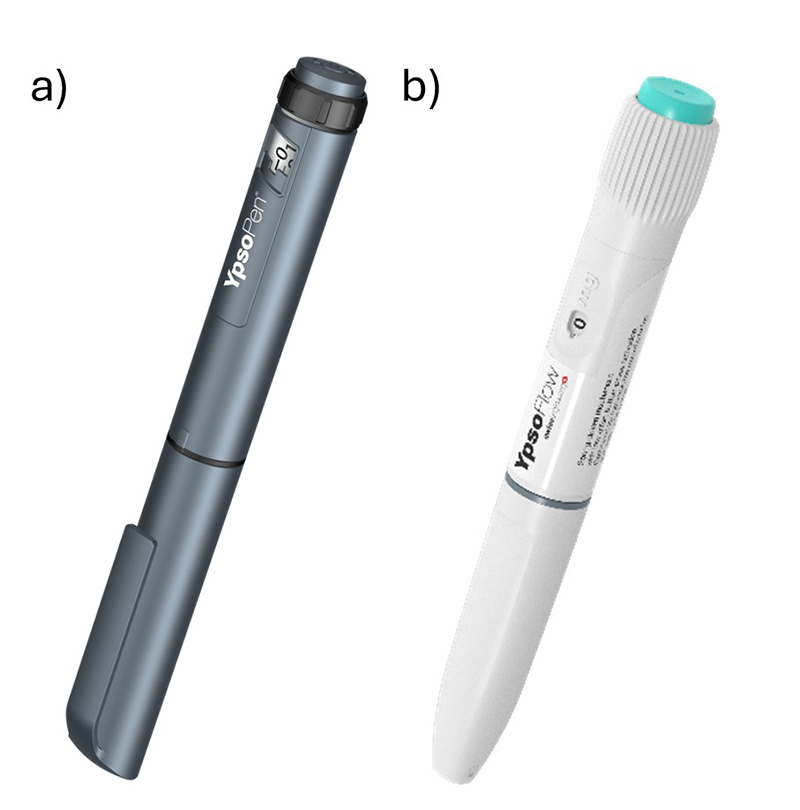

Ypsomed, the Ypsomed logo, YpsoPen® and YpsoFlow™ are trademarks of Ypsomed AG. © 2025 Ypsomed AG. All rights reserved. Product images shown are the property of Ypsomed AG and used with permission.
Industry-Wide Effects
The disruption caused by anti-obesity drugs extends beyond the pharmaceutical industry. The food and beverage sector, for instance, is expected to experience changes in consumer behavior, with GLP-1 users consuming approximately 8% less food. JPMorgan predicts a 3% reduction in overall food consumption by 2030, accompanied by a shift toward higher-quality foods rather than greater quantities. Similarly, the wellness industry—including gyms and plastic surgeons—is likely to see increased demand for services related to weight management and overall health (4,5).
Challenges and Investments
The approval of anti-obesity drugs has led to significant investments across the industry to meet market demand. Companies such as Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly and Company (Lilly) have invested billions in expanding their manufacturing capacities. Novo Nordisk, for example, has invested $4.1 billion in a plant in North Carolina and acquired Catalent plants in Belgium, Italy and the US Lilly has invested $9 billion in a site in Lebanon, Indiana and is developing new plants in Germany and the Research Triangle Park in North Carolina (8-10).
Reimbursement and Accessibility
Reimbursement for anti-obesity drugs remains a critical issue, with pricing varying significantly across geographic regions. In the US, insurance coverage for Wegovy is estimated at around 40%, while in non-U.S. markets, the drug is primarily paid for out-of-pocket. Economists at the University of Southern California estimate that reimbursing obesity drugs could save $1 trillion over the next decade, highlighting the importance of making these treatments accessible to lower-income populations.
Future Directions
 The future of anti-obesity drug delivery includes exploring various methods beyond disposable prefilled syringes, such as reusable
injectors, cartridge-based pens, oral delivery, nasal delivery, implants and hydrogel technology. Each method has its pros and cons, with considerations for sustainability, user-friendliness, and clinical efficacy (7).
The future of anti-obesity drug delivery includes exploring various methods beyond disposable prefilled syringes, such as reusable
injectors, cartridge-based pens, oral delivery, nasal delivery, implants and hydrogel technology. Each method has its pros and cons, with considerations for sustainability, user-friendliness, and clinical efficacy (7).
Conclusion
The introduction of new injectable anti-obesity therapies is set to revolutionize drug delivery and impact various industries. With significant market growth, industry-wide investments and ongoing developments in drug delivery methods, the future of anti-obesity treatments looks promising. Ensuring accessibility and reimbursement for these drugs will be crucial to addressing the global obesity epidemic and improving overall health outcomes.
References
- Berger L.; Linvill E. SHL Molly® Autoinjectors: Powering the Next Wave of Cardiometabolic Care. ONdrugDelivery [Online], 2024, 160, 42–46. https://www.ondrugdelivery.com/shl-molly-autoinjectors-powering-the-next-wave-of-cardiometabolic-care/#:~:text=Lars%20Berger%20and%20Eric%20Linvill%20discuss %20the%20rapid,meet%20the%20challenges%20presented%20by%20this%20disease%20area (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Biasio, L.; Skibba, G. Sustainable GLP-1 Drug Delivery: Future-Proofing Therapy Administration for Obesity and Beyond. ONdrugDelivery [Online], 2025, 171, 14-20. https://www.ondrugdelivery.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/171_2025_AprMay_ Sustainability_Ypsomed.pdf (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Zhu K.; Kakkar R.; Chahal D.; Yoshida E. M.; Hussaini T. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol [Online], 2023, 29(37), 5327-5338. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10600803/ (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Gladstone, A. WeightWatcher Prepares for Bankruptcy. WSJ [Online]. 2025. https://www.wsj.com/articles/weightwatchers-prepares-for-bankruptcy4c81b69f? msockid=3acc69f66eca6ff31be47a586fa26e80 (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- WeightWatchers Takes Strategic Action to Eliminate $1.15 Billion of Debt, Strengthening Financial Position for Long-Term Growth and Profitability. WeightWatchers. 2025. https://corporate.ww.com/news/news-details/2025/WeightWatchers-TakesStrategic-Action-to-Eliminate-1-15-Billion-of-Debt-Strengthening-FinancialPosition-for-Long-Term-Growth-and-Profitability/default.aspx (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Rigby J. Exclusive: WHO to back use of weight-loss drugs for adults globally, raises cost issue. Reuters [Online]. 2025. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcarepharmaceuticals/who-set-back-use-weight-loss-drugs-adults-globally-raises-cost-issue2025-05-01/ (accessed on June 26, 2025
- Lilly's oral GLP-1, orforglipron, demonstrated statistically significant efficacy results and a safety profile consistent with injectable GLP-1 medicines in successful Phase 3 trial. Eli Lilly. 2025. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/newsrelease-details/lillys-oral-glp-1-orforglipron-demonstrated-statistically (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Fick M.; Gronholt-Pedersen, J.; Jacobsen S. Novo Nordisk ousts CEO after falling behind in weight loss market. Reuters [Online]. 2025. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/novo-nordisk-ceo-stepdown-2025-05-16/ (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Novo Nordisk A/S: Lars Fruergaard Jørgensen to step down as CEO of Novo Nordisk. Novo Nordisk. 2025. https://www.novonordisk.com/content/nncorp/global/en/news-and-media/news-and-irmaterials/news-details.html?id=916007 (accessed on June 26, 2025)
- Waldron, J. Novo Nordisk pens $2B deal for triple G agonist tied to 15% weight loss at 12 weeks. Firece Biotech [Online]. 2025. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/novo-nordisk-pens-2b-deal-triple-g-agonist-tied15-weight-loss-12-weeks (accessed on June 26, 2025)



