PDA Standards Development
PDA Catalog of Technical Documents
View HereIn a heavily regulated industry, it is imperative to follow accepted rules, guidelines, and ways of doing things to improve processes and reduce regulatory risk.
A standard is established by consensus and provides rules, guidelines, or characteristics for activities or their results. Implementing standards enables organizations to streamline processes, reduce costs, gain and maintain market access, and boost their bottom lines.
PDA has been accredited as a standards developing organization by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) since 2017. PDA’s standards program focuses on documentary standards, building on the existing rigorous, volunteer expert-driven scientific process used to develop PDA’s technical reports.
Why Have Standards
Standards serve a very important purpose and are a part of our daily lives − in the lab where our samples are tested, in the equipment that we use at the gym, to the way we work and perform our jobs. We need them to help keep us safe, to make sure that there is consistency in how products are made, tested, and used by all, and sometimes the government may mandate compliance with a standard in lieu of government guidance. Standards benefit everyone too—industry, government, consumers, young professionals, and students.
 PDA is recognized by industry professionals and regulators around the world who rely on PDA’s peer-reviewed technical documents for expert guidance and opinions on important scientific and regulatory topics.
PDA is recognized by industry professionals and regulators around the world who rely on PDA’s peer-reviewed technical documents for expert guidance and opinions on important scientific and regulatory topics.
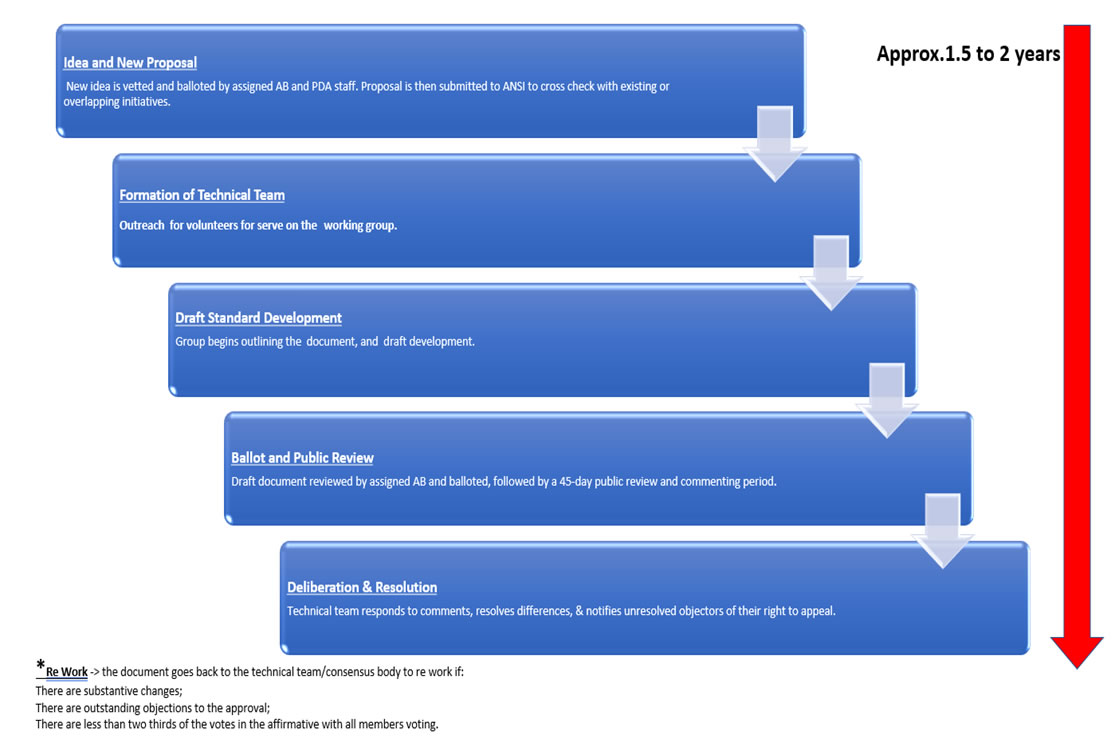
The PDA became a Standards Developing/Development Organization (SDO) through the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). ANSI is a private, non-profit 501(c)(3) organization whose mission is “to enhance both the global competitiveness of U.S. business and the U.S. quality of life by promoting and facilitating voluntary consensus standards and conformity assessment systems and safeguarding their integrity.” ANSI does make it easier to come to an agreement by accrediting the procedures used by standards developers, and by making sure that these procedures allow for openness, balance, consensus, and due process.
Approval of a PDA standard as an American National Standard (ANS) means that the standard meets ANSI’s Essential Requirements and the Federal government’s definition of a Voluntary Consensus Standard per OMB A119, and the World Trade Organization (WTO) Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Code of Good Practice (CGP) criteria for openness, transparency, impartiality and consensus, relevance and effectiveness.
PDA Standards are Intended to be Scientifically Derived Technical Standards. Examples Include:
- Material quality standards – this may describe tests, specifications, or data conversion on specified materials.
- Universal Process & procedure standards – This may be an agreed upon processes in the industry or agreed upon way of doing something.
- Format or Referencing standard – This could be an agreed upon list of definitions, nomenclature, or data formats to facilitate global harmonization in scientific language.
- Measurement/ Metrology standards - Supports harmonization in equipment use, statistical calculations, and formulas.
Becoming an accredited Standards Developer means that the process and steps performed by PDA meet the guidelines set forth by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in the ANSI Essential Requirements: Due Process Requirements for American National Standards. The key elements include openness, consensus vote, due process, lack of dominance, balance, public review/consideration of views and objections, an appeals process, and compliance with the ANS policies and administrative procedures.
Important
As a reminder, all draft documents are copyrighted and neither this publication nor any portion thereof maybe adapted, copied or otherwise reproduced by electronic, mechanical, photocopying or recording without prior written permission from PDA SDO.
To request permission to use this publication or any portion thereof in any manner, please contact PDA .
Learn More about PDA Standards:
 Another advantage in becoming an ANSI-accredited Standards Developer and having approved standards through ANSI is that the voluntary consensus standards are produced in a process consistent with that of the International
Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Another advantage in becoming an ANSI-accredited Standards Developer and having approved standards through ANSI is that the voluntary consensus standards are produced in a process consistent with that of the International
Organization for Standardization (ISO).
ANSI is the sole U.S. representative of ISO, and a founding member; hence, ANSI plays an active role in ISO governance. ANSI has also been a strong and active leader in ISO’s sister organization, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), as well as other international and regional standardization bodies. By being accredited through ANSI, PDA has the opportunity to also participate in ISO standards development.
Membership in any PDA standards development activity is open to everyone, particularly those that may be interested or involved in production, application, and regulation of products related to the pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, scientific, and regulatory community. The PDA SDO recognizes 4 Interest categories:
- Producer - An individual or organizational representative, is involved in the commercial production, promotion, sale, use or distribution of materials, products, systems, or services covered in the scope of technical documents developed by PDA shall be classified as an Producer Interest stakeholder. Individuals in this interest category include manufacturers, those involved in supply chains, employees of test labs or commercial labs, etc.
- User - An individual or organizational representative, purchases, utilizes or receives the materials, products, systems, or services covered in the scope of technical documents developed by PDA in the delivery of pharmaceuticals shall be classified as a User Interest stakeholder. Individuals in this interest category include employees or representatives of pharmaceutical manufacturing organizations, patients, etc.
- General Interest - An individual or organizational representative, has a general interest in the materials, products, systems, or services covered in the scope of the technical documents developed by PDA and who does not fit into any of the preceding categories shall be classified as a General Interest stakeholder. Individuals in this category would include noncommercial academicians, noncommercial researchers, patient or consumer advocates, representatives of accrediting organizations, representatives of other organizations, etc.
- Regulator - An individual or organizational representative, is involved in the regulation of the materials, product, systems, or services covered in the scope of the technical documents developed by PDA shall be classified as a Regulatory Interest stakeholder. Individuals in this interest category would include those representing federal, state, local, foreign, or other government entities
We encourage you to read more in understanding how standards support business: www.standardsboostbusiness.org, by contacting [email protected], and make sure to visit the Frequently Asked Questions page.
Read more about how standards support business – https://www.standardsboostbusiness.org
Contact Us: For questions on PDA Standards or to get involved in the process, please contact us at [email protected]
Standards Completed
- PDA/ANSI Standard 06-2025: Assessment of Quality Culture Guidance Documents, Models, and Tools
- ANSI/PDA Standard 02-2021, Cryopreservation of Cells for Use in Cell Therapies, Gene Therapies, and Regenerative Medicine Manufacturing: An Introduction and Best Practices Approach on How to Prepare, Cryopreserve, and Recover Cells, Cell Lines,
and Cell-Based Tissue Products.
Brian Hawkins (Chair), Kathy Loper (Co-Chair) - ANSI/PDA Standard 04-2021, Phage Retention Nomenclature Rating for Small and Large Virus Retentive Filters.
Duncan Low (Chair), Scott Lute (Co-Chair) - ANSI/PDA Standard 05-2021, Consensus Method for Rating 0.1 Mycoplasma Reduction Filters.
Martha Folmsbee (Chair), Kathleen Souza (Co-Chair) - PDA/ANSI Standard 03-2025: Standard Practice for Quality Risk Management of Aseptic Processes.
Noel Long (Chair), Amanda Bishop- Mcfarland (Co-Chair)
Standards in Development
- PDA Standard 01-2020:, Enhanced Purchasing Controls to Support the Bio-Pharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, Medical Devices and Combination Products Industries. Martin Van Trieste (Chair), Sue Schniepp (Co-Chair).
- BSR/PDA Standard 07-202x, Analytical Procedure Replacement, Transfer and the Use of Analytical Platform Procedures for Biologics (new standard). Stephan Krause (Chair), Jayda Siggers (Co-Chair)
- BSR/PDA Standard 08-202x, Guidance for Manufacturers: Apheresis Collections for Cell and Gene Therapy Products (new standard). Dr. Catherine B. Zander, Chair, Tracey Hlucky (Co-Chair- Kite)
New Standard Initiatives
- Coming Soon
Below is a routinely updated schedule of the consensus body meetings that reflects PDA’s commitment to engaging and leveraging its members and experts across the industry in the review, updating and development of its standards.
Meeting attendance is free and open to the public, but registration is required.
Register Now
If you have any questions or comments about PDA’s standards focused meetings, please email [email protected].
Standards in Development
- BSR/PDA Standard 07-202x, Analytical Procedure Replacement, Transfer and the Use of Analytical Platform Procedures for Biologics (new standard). Stephan Krause (Chair), Jayda Siggers (Co-Chair)
Next consensus body meeting - Biweekly starting January 6, 2025 via MsTeams - BSR/PDA Standard 08-202x, Apheresis Collection for Cell and Gene Therapy Products (new standard). Dr. Catherine B. Zander, Chair, Tracey Hlucky (Co-Chair- Kite)
Next consensus body meeting - Biweekly starting January 8, 2025 via MsTeams
Latest PDA Standards
-

PDA/ANSI Standard 06-2025: Assessment of Quality Culture Guidance Documents, Models, and Tools
PDF Single userMember price: $180.00 Nonmember price: $325.00 -

PDA/ANSI Standard 03-2025: Standard Practice for Quality Risk Management of Aseptic Processes
PDF Single userMember price: $180.00 Nonmember price: $325.00 -

ANSI/PDA Standard 02-2021: Cryopreservation of Cells for Use in Cell Therapies, Gene Therapies, and Regenerative Medicine Manufacturing
PDF Single userMember price: $135.00 Nonmember price: $243.75
Please sign in or become a member to purchase items from the PDA bookstore.